The Dawn of Precision: Robotic Surgery in Urology
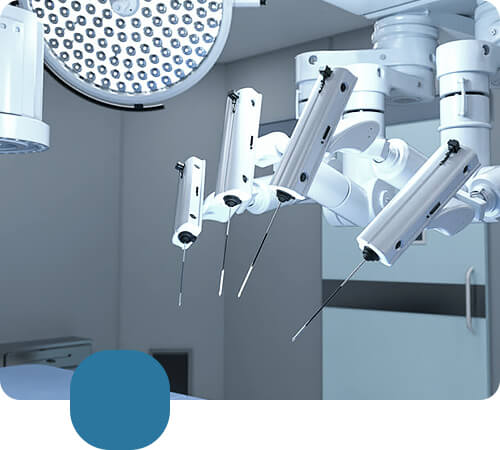

Robotic surgery has rapidly emerged as a groundbreaking technology within the sphere of urology, signaling a new era of precision and refined techniques for complex procedures. This innovative approach leverages robotic systems, granting surgeons unparalleled control, superior vision, and dexterity beyond the capabilities of the human hand alone. By integrating sophisticated robotics, urologic surgery now encompasses a minimally invasive paradigm, minimizing the physical trauma traditionally associated with surgical interventions.
The evolution of this technology has been fueled by the quest to surmount the intrinsic limitations of conventional urological surgeries, which are often characterized by significant blood loss, pain, and extended recovery periods. Robotic platforms, equipped with high-definition, three-dimensional visualization, allow for meticulous dissections and suturing, thus, enhancing surgical accuracy. This leap in precision facilitates the performance of complex reconstructive procedures with enhanced finesse, dramatically reducing the occurrence of postoperative complications and improving overall surgical margins.
| Aspect | Traditional Surgery | Robotic Surgery in Urology |
|---|---|---|
| Incision Size | Larger, more invasive | Smaller, minimally invasive |
| Recovery Time | Longer due to greater tissue disruption | Reduced, with fewer complications |
| Visualization | Limited 2D view | Enhanced 3D, high-definition view |
| Manual Dexterity | Limited by human hand | Enhanced by robotic articulation |
In the context of this technological renaissance, the pivotal shift toward robotic surgery in urology represents more than just a technological triumph; it epitomizes a transformation in surgical philosophy. This ethos embodies a commitment to patient-centered care, opting for procedures that promise less pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker return to normal activities. As the field continues to evolve, the convergence of engineering innovations with medical expertise paves the way for an era where surgical outcomes are significantly improved, aligning with the highest standards of patient care.
Overcoming the Limitations of Traditional Surgical Approaches
Robotic surgery in urology represents a transformative evolution beyond traditional surgical methodologies, addressing their inherent limitations with remarkable precision and flexibility. Traditional urological procedures have long been confined by the finite dexterity of the human hand and the constraints imposed by open surgery or laparoscopy. These limitations often resulted in significant postoperative pain, longer hospital stays, and extensive recovery periods for patients. Moreover, the challenges of visualizing complex anatomical areas and executing precise maneuvers in confined spaces further complicated these interventions, affecting both outcomes and patient experiences. By integrating robotic systems, surgeons are now endowed with enhanced capabilities, such as three-dimensional magnification and articulated instrument movement, which significantly mitigate these challenges.
The introduction of robotic surgery into what is modern urology has catalyzed a paradigm shift in the treatment of urological conditions. Surgeons equipped with robotic tools can execute procedures with unparalleled precision, ensuring minimal invasiveness. This has profound implications for patient care, notably through reduced intraoperative blood loss, diminished pain, and lower risks of infection. These advances not only improve patient comfort and safety but also contribute to a faster return to normal activities, marking a significant leap in enhancing patient outcomes. The ability to perform complex surgeries through smaller incisions exemplifies how robotic technology is setting new standards in surgical care, making the unthinkable routines a reality.
The incorporation of robotics into urological surgery not only transcends the physical and technical limitations faced by surgeons but also ushers in a new era of surgical education and skill acquisition. As practitioners navigate the learning curve of this advanced technology, the broader healthcare ecosystem reaps the benefits of accelerated recovery times and optimized surgical precision. This elevates the standard of care in urology, enabling a future where robotic-assisted procedures become the cornerstone of effective, patient-centered treatment strategies. The continuous refinement and integration of robotic systems in urology signify a progressive step towards overcoming the constraints of traditional surgery, heralding a future where health outcomes are significantly enhanced through technological innovation.
The Role of Robotics in Enhancing Patient Outcomes
In the vanguard of medical advancements, robotic surgery emerges as a transformative force within the sphere of urology, redefining what is modern urology. This integration of robotics is pioneering a new era of precision, where the minutiae of surgical operations are executed with an unprecedented level of accuracy. This shift is significantly improving patient outcomes, as surgeries performed with robotic assistance are generally associated with reduced recovery times, minimized risk of infection, less postoperative pain, and notably smaller scars. Such advancements not only enhance the patient's physical well-being but also ameliorate their psychological recovery, considering the reduced physical evidence of surgery and quicker return to daily activities.

Moreover, the use of robotic systems in urological procedures has been instrumental in the shift towards more conservative and organ-sparing surgeries, which inherently preserve organ function and improve the quality of life. This is particularly relevant in cancer surgeries, where precision is paramount in removing malignant tissues while safeguarding the surrounding healthy structures. The dexterity and high-definition 3D visualization offered by robotic platforms enable surgeons to achieve this delicate balance with greater confidence. Consequently, patient outcomes extend beyond the immediate postoperative period, influencing long-term health and functional preservation in ways traditional methods could scarcely achieve.
Navigating through the complexities of prostatectomies, cystectomies, and kidney surgeries, robotic technology stands as a beacon of hope for patients, offering a less invasive option with compelling evidence of improved clinical outcomes. As healthcare continues to evolve, the role of robotics within urology is a testament to the relentless pursuit of excellence in patient care. The ongoing research and development promise not only to refine these technologies further but also to make them more accessible. This democratization will likely amplify their positive impact, ensuring that a greater number of patients globally can benefit from the enhancements in surgical precision, safety, and overall recovery that robotic surgery offers.
Navigating the Learning Curve: Surgeons Embracing Technology
The integration of robotic technology into the realm of urological surgery represents a paradigm shift, confronting surgeons with a steep yet rewarding learning curve. As practitioners embark on this technological journey, the mastery of robotic systems is becoming an indispensable skill set in modern urology, facilitating minimally invasive procedures with precision unmatched by conventional techniques. This evolution necessitates an immersive educational experience, merging hands-on training with virtual reality simulations, to cultivate a deep understanding of robotic mechanics and software nuances. The challenge lies not only in the technical adoption but also in developing the cognitive skills to execute complex surgical maneuvers through a robotic interface, underscoring the transformation from manual dexterity to digital prowess.
Furthermore, the embrace of robotic technology by the surgical community has underscored the importance of continuous education and adaptive learning frameworks. Academic institutions and healthcare organizations are increasingly investing in specialized training programs, workshops, and fellowships focused on robotic surgery, aiming to shorten the learning curve while maintaining high standards of patient care. Such initiatives are critical in fostering a culture of innovation, encouraging surgeons to push the boundaries of what is modern urology. By nurturing a proficient workforce adept in robotic surgery, the medical field is setting a new benchmark for excellence, enhancing surgical outcomes, and reducing the margin of error.
The transition towards robotic-assisted surgery in urology, while daunting, presents an exciting horizon of opportunities for both surgeons and patients. As technology advances, the scope of what is feasible within the confines of the operating room expands, promising a future where surgical interventions are characterized by superior precision, reduced invasiveness, and optimal patient recovery times. This dynamic shift underscores the significance of embracing change and committing to lifelong learning, demystifying the complexities of robotic systems, and redefine the surgical landscape in urology. The journey through the learning curve is not merely an adoption of new tools but a reinvention of surgical philosophy and practice, heralding a new era in healthcare innovation.
The Economic and Social Impact of Robotic Urology
The advent of robotic technology in the medical field has remarkably revolutionized what is modern urology, transcending the traditional boundaries to redefine efficiency and precision. This transformation is not only confined within the operational theatrics but extends its reach towards economic and social domains, bringing forth a nuanced perspective on healthcare delivery. Economically, the integration of robotic systems in urological procedures, despite its high initial investment, has demonstrated the potential to reduce long-term healthcare costs. This reduction is primarily attributed to shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and decreased necessity for follow-up surgeries, all of which contribute to a more cost-effective healthcare model. Moreover, the precision of robotic surgery minimizes the risk of complications, further curtailing the financial burden on both healthcare systems and patients.
The social implications of robotic urology are equally profound, as they pivot on improving patient quality of life and democratizing access to advanced care. Patients who undergo robotic-assisted surgery often experience less post-operative pain, reduced scarring, and quicker return to daily activities, enhancing the overall patient experience and satisfaction. Additionally, the technology's ability to facilitate minimally invasive procedures opens the door for patients, who might have been deemed ineligible for conventional surgery due to health constraints, to receive necessary treatments. This inclusivity not only broadens the scope of those who can benefit from high-quality urological care but also underscores a significant shift towards patient-centered medicine.
Charting the course for future economic and social ramifications, it is imperative to consider the ongoing refinements and accessibility of robotic technology. As these systems become more widespread and integrated into different facets of urology, their impact is expected to amplify.
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Economic | Reduction in healthcare costs due to fewer complications, shorter hospital stays, and less need for follow-up surgeries. |
| Social | Enhanced patient experience through less invasive procedures, quicker recovery, and expanded access to advanced surgical interventions. |
This dual-pronged impact not only elevates the standard of care within urology but also underscores the role of advanced technologies in shaping a more efficient, inclusive, and patient-centered healthcare landscape.
Future Frontiers: Innovations Shaping Robotic Urological Surgery
The landscape of urological surgery is on the brink of transformative change, spearheaded by innovations in robotic technology. With advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, robotic systems are becoming more intuitive, offering surgeons unprecedented precision and control. This evolution is not merely about enhancing surgical tools but integrating comprehensive data analytics to personalize patient care. Future iterations of robotic surgery will likely feature systems capable of real-time imaging analysis, enabling surgeons to make more informed decisions during procedures. The incorporation of virtual reality (VR) for training and planning purposes exemplifies how digital twins of patients could revolutionize pre-surgical strategies, allowing for rehearsals of complex surgeries in a risk-free environment.
On the horizon, the miniaturization of robotic tools promises to push the boundaries of minimally invasive surgery even further. Microbots, guided by magnetic fields or even within the bloodstream, could perform targeted therapies or biopsy procedures with minimal patient discomfort and reduced recovery times. Moreover, the integration of haptic feedback mechanisms in robotic systems will allow surgeons to 'feel' the tissue through the robotic interface, mimicking the tactile response of traditional surgery but with the enhanced precision and flexibility that robotics allow. This leap in technology underscores a paradigm shift towards an era where the surgeon's role evolves, focusing more on strategic intervention while leveraging AI for routine tasks and analysis.
As we advance, the ethical and regulatory landscape surrounding robotic surgery will also need to evolve. Ensuring these technologies are accessible and beneficial across diverse populations remains a critical challenge. The promise of robotic urological surgery lies not only in its technological marvels but in its potential to democratize high-quality care, reducing disparities in surgical outcomes. Thus, embracing these innovations requires a concerted effort from policymakers, medical professionals, and the tech community to navigate the complexities of integrating such sophisticated tools into the fabric of healthcare, ensuring they enhance, rather than replace, the human elements of medicine.